 |
| |
C# WinApp สอบถามวิธีใช้งาน unsafe ครับ พอผมก๊อบโค้ดมาวางก็ ขึ้น Error โดยที่ยังไม่ได้เขียนอะไรเพิ่มเลย |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Date :
2016-12-07 09:15:04 |
By :
lamaka.tor |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
คุณก็เข้าไปอ่านบทความของคุณ "ลาบเป็ด" (เขาอธิบายได้ชัดเจนตรงไปตรงมา[ไม่ง่ายที่จะอธิบายได้แบบนี้])
Unsafe == Pointer นั่นแหละ (ภาษาสมัยเก่าก็ยังมีเลย 20 ปีมาแล้วมั้ง) เช่น
FoxPro/Visual FoxPro
Code (VB.NET)
Store "DO FORM frmXXX" TO fpdPointer
&fpdPointer //มันทำงาน === frm.Show() นั่นแหละ
//นี่ก็คือ Pointer
สิ่งที่บางคนยังสงสัยว่า VB.NET มี Pointer หรือไม่?
--- มีแน่นอน แต่ว่า MS ไม่ได้เขียนเอกสารกำกับเอาไว้ (Unleaded VB.NET)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Date :
2016-12-07 14:30:07 |
By :
หน้าฮี |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
Code (C#)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Unsafe
{
class Program
{
unsafe static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] x = new int[10]; // x.Length = 10 All Value = 0
unsafe {
int* p1, p2, p3; // OK
//int *p1, *p2, *p3 ; Invalid in C#
int a;
int* b;
//int c, *b; Invalid in C#
a = 25;
b = &a;
int i = 7;
// Unsafe method: uses address-of operator (&):
SquarePtrParam(&i);
Console.WriteLine("b = {0}", *b);//returns b = 25
Console.WriteLine("i = {0}", i); //returns i = 49
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
// Unsafe method: takes pointer to int:
unsafe static void SquarePtrParam(int* p)
{
*p *= *p;
}
static void test()
{
String a = "Hello World";
String b = a;
a = "Hello";
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", a, b); // Hello, Hello World
Console.WriteLine(a == b); //false
Console.WriteLine(object.ReferenceEquals(a, b)); //false
}
}
}
ปล. อันนี้ทำเก็บเอาไว้ตั้งนานนมแล้วนะ (จนนมไขว้หลังได้)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Date :
2016-12-07 14:51:58 |
By :
หน้าฮี |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
ผมงงตรงที่ว่า ทั้งๆที่ผมก็ก๊อบโค้ดมาโดยที่ยังไม่แก้อะไรเลย
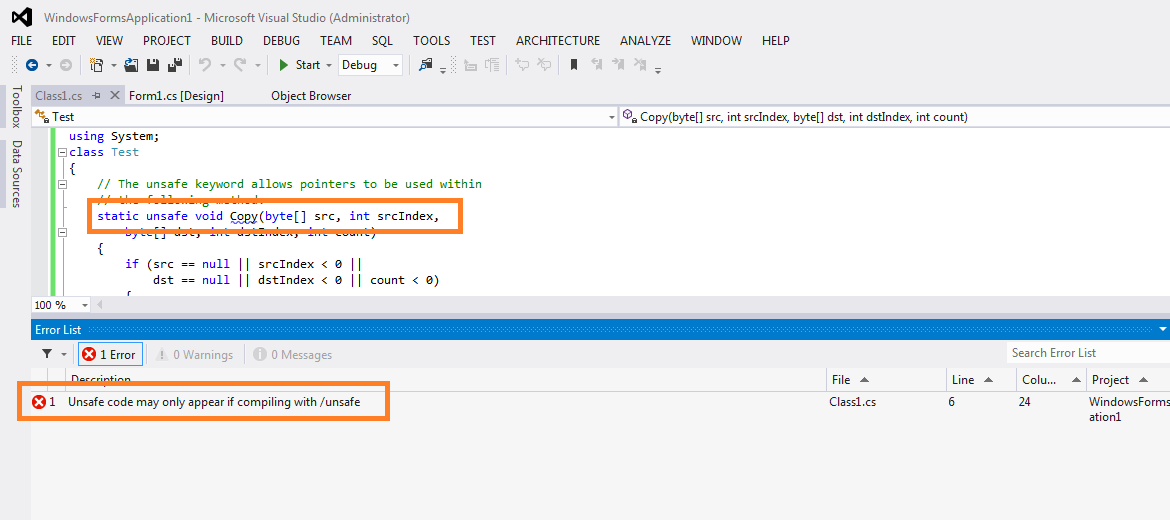
แต่กลับรันโค้ดไม่ได้ครับ
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Date :
2016-12-08 23:43:38 |
By :
lamaka.tor |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
ผมเข้าใจในวัตถุประสงค์ของ MS Product (Visual Studio/etc...)
แต่ผมไม่เข้าใจในความต้องการของคุณ
[x] Allow unsafe code
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Date :
2016-12-10 19:52:02 |
By :
หน้าฮี |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
มารื้อปัญหาเก่าอีกแล้วครับ
ตกลง unsafe ใช้ยังไงกันแน่รึครับ
วันนี้ก๊อบโค้ดมาเจอ error unsafe อีกแล้วครับ
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Date :
2017-04-26 16:16:20 |
By :
LAMAKA |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
หลังจากลองผิดลองถูกซักพักก็ได้แล้วครับ
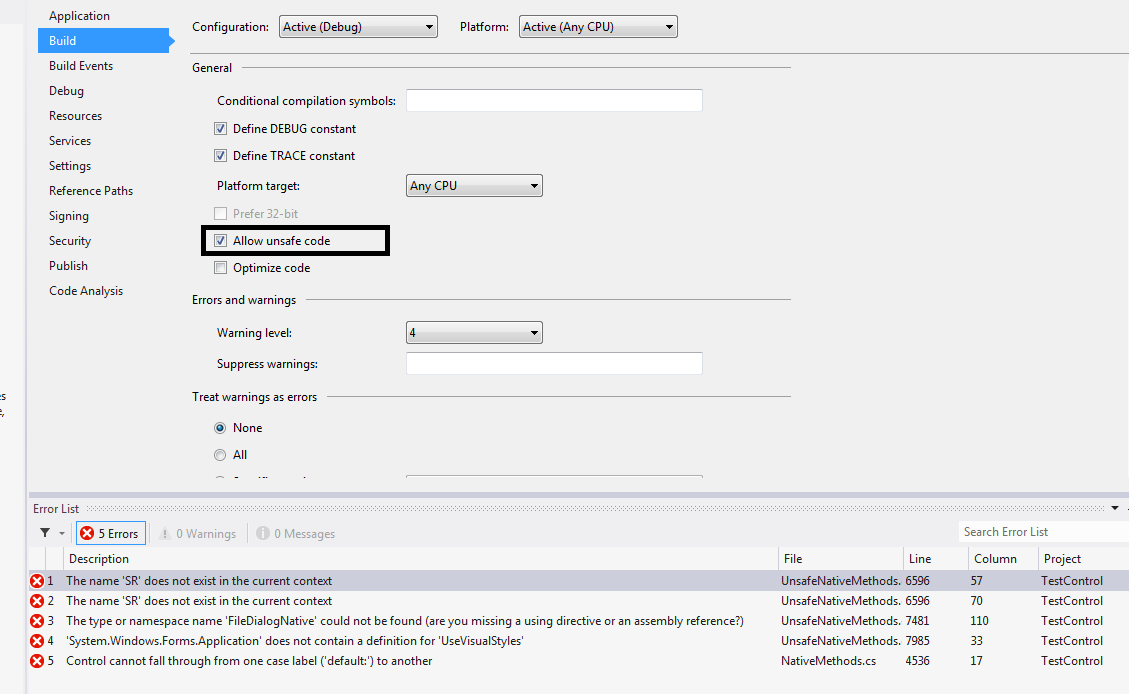
ต้องขอบคุณท่าน หน้าฮี จาก No. 5 ครับ
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Date :
2017-04-26 16:25:17 |
By :
LAMAKA |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
แต่ก็ยังสงสัยว่า
SR มันคืออะไร
ท่านใดที่แกะโค้ด .net อยู่ บ้างครับ
ผมอยากรู้ว่า
SR มันคืออะไร แล้วจะเอามาจากไหนครับ
Code (C#)
protected static void NotImplemented() {
ExternalException e = new ExternalException(SR.GetString(SR.UnsafeNativeMethodsNotImplemented), NativeMethods.E_NOTIMPL);
throw e;
}
ดูใน .net เองก็ไม่มีอ้างอิงเหมือนกัน กรรม แท้ๆ ช่วงนี้
ปกติเราเอาเม้าไปชี้ จะมี อ้างอิงมาบอกว่า อยู่ตรงไหน
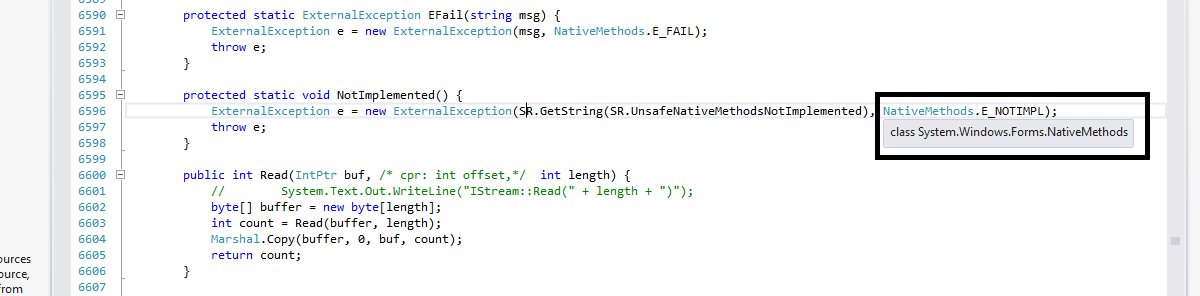
แต่ SR เงียบไปเลย มิดปานหอยไข้
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Date :
2017-04-26 16:38:22 |
By :
lamaka.tor |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|